Kanban
Kanban is the Japanese word for signal. In a Lean production system, a kanban is a signal that pulls material into the production sequence as needed. With a kanban system, material is not pushed into the production system. Inventory is minimized and production flow improves.
Kanbans are used to regulate production and material replenishment. They are most effective when they are a simple and visual. They can eliminate the need for a master production schedule because at each step of the process, material is pulled in as needed according to the takt time.
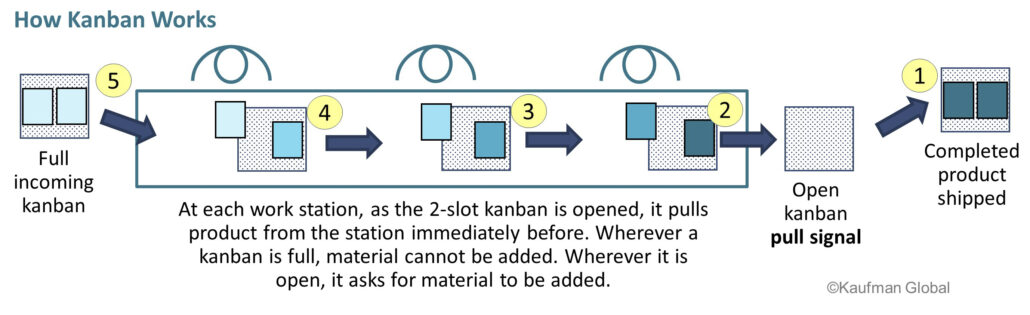
A kanban signal can be a card that indicates “Need New Material Now” because the material that was at this point in the line has been pulled into the next step in the process. Or sometimes a kanban is simply an open marked area on the floor or shelf that shows nothing is sitting there, but since it is now open, it is a kanban signal saying “material needed here!”
A kanban tells the production / replenishment process
- What to produce / replenish
- When to produce / replenish
- How many to produce / replenish
- Where the material must be delivered
- Visual and easily understood
- Local ownership – “operator to operator” communication
What Kanbans Do
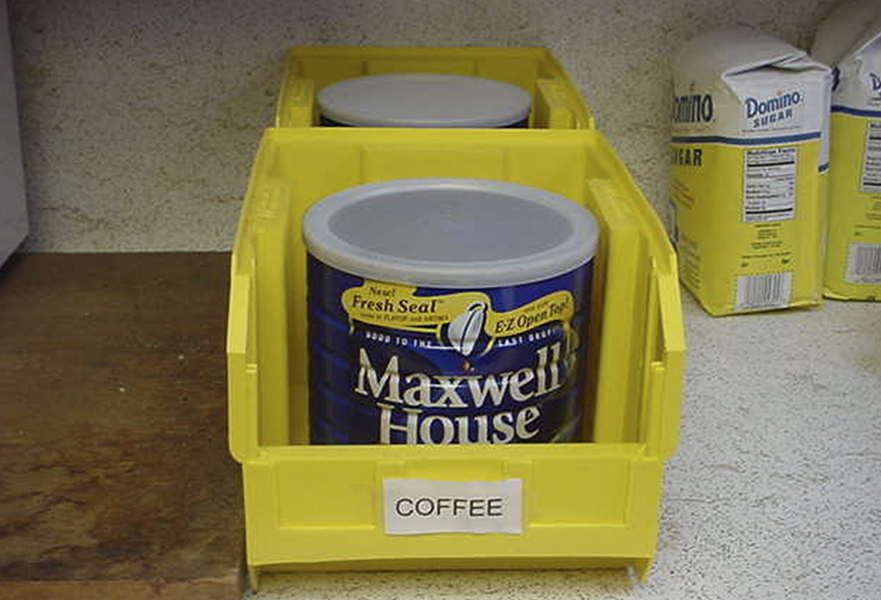

Kanbans regulate production and material replenishment in a lean production system. “In-process” kanbans link adjacent processes in a pull production system to ensure timely production of parts and eliminate overproduction. “Material” kanbans are used to trigger material replenishment from the store or external / internal suppliers as required.
Why Kanbans are Helpful
Kanbans are a simple and visual way of regulating production and material replenishment such that each process produces / replenishes only what is consumed by the downstream process. As such, they:
- Eliminate overproduction / over replenishment
- Minimize parts shortages
- Minimize errors and confusion over what to produce / order, when to produce / order it and in what quantity.
